If you are at risk of a foot injury in your workplace, you should implement a foot safety protection program.
Beyond fashion or personal style, the choice of appropriate footwear is essential to prevent both potential hazards and workplace accidents. Wearing the right type of footwear not only protects employees from injuries but also enhances their comfort and overall well-being during long working hours. The correct shoes or boots can provide stability, support, and protection against specific workplace risks, making them an indispensable aspect of occupational health and safety protocols.
Selecting Footwear
1. Determine the risks involved for each job by completing a risk assessment.
2. Determine the basic criteria required to protect the worker.
3. Write and communicate the program requirements (education/training is recommended).
4. Select comfortable shoes!
Risk Assessment:
Hazards To Consider:
Safety Hazard
– Objects falling onto or striking the feet.
– Sharp or pointed objects that might cut the top of the feet.
– Objects that can puncture the bottom or side of the foot.
– Material or equipment that might roll over the feet.
– Exposure to rotating or abrasive machinery
Physical Hazard
– Type of walking surface (slips and trips), including loose ground cover, smooth surfaces, or wet/oily surfaces.
– Exposure to extreme hot or cold.
– Risk of contact with energized conductors.
– Possible explosive atmospheres (static electrical discharges).
– Sensitive electronic components or equipment (discharge of static electricity).
Chemical & Biological Hazard
– Water or other liquids that may penetrate the footwear.
– Exposure to corrosive or irritating substances.
Ergonomic Hazard
– Standing or sitting for long periods of time.
– Contact stresses to the feet.
– Back, hip, knee and ankle pain (extensive to chronic).
Controls (PPE) To Implement
Consider where and when specific types of footwear are required. These are examples of the type of footwear that can be designated within the workplace to protect workers from hazards.
– No perforated shoes, sandals and the like.
– Heels shall not exceed 1 inch and shall have at least a 1” square base on the heel.
– Closed toe/foot shoes.
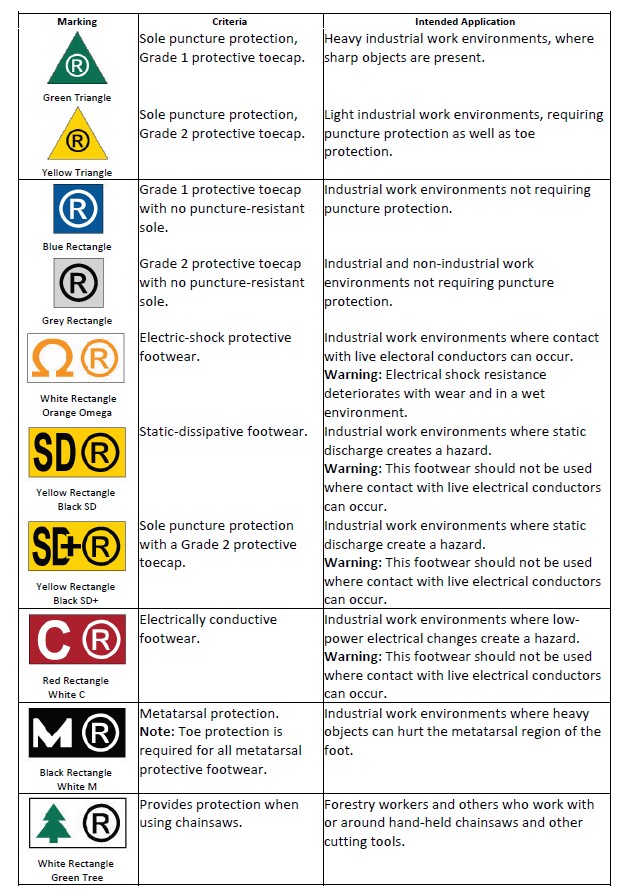
– Work boots, criteria specific (see chart below; article continues below chart)
Fit Tips
– Try on new boots around midday, feet normally swell during the day.
– Walk in new footwear to ensure it is comfortable.
– Boots should have toe room, DO NOT expect footwear to stretch with wear.
– Make allowances for extra socks or special arch supports when buying boots.
– Boots should fit snugly around the heel and ankle when laced.
– Lace up boots fully.
Related Legislation
Federal
Canada Occupational Health and Safety Regulations
– Part XII Protection Equipment and Other Preventive Measures (12.11 Protective Footwear)
Provincial
Manitoba Workplace Safety and Health Act
– 45.2 INAPPROPRIATE OR UNSAFE FOOTWEAR
Workplace Safety And Health Regulation
– Part 6 PPE (6.12 Footwear: responsibilities of employers and workers)
RPM offers a number of courses to help support your OHS plan. If this article was valuable to you or others at your organization, you may want to consider the following Program Development courses:
Workplace Inspection Training will give people the opportunity to explain the requirements and the purpose(s) of a workplace inspection, know what you’re looking for and how to identify a hazard, recognize the process of what to do when there are inspection findings, and understand the process for implementing corrective actions and how to monitor and identify trends.
Hazard Identification and Risk Control – Recognizing what could injure workers on the job is the first step to ensuring that they stay safe. A proactive approach to the mitigation of workplace hazards greatly increases the chance of less severe and lower rates of injury. This course will provide students with the practical knowledge necessary to identify, assess and control the hazardous elements of their workplace so they can do their part in preventing dangerous incidents.
Slips, Trips, Falls, Sprains and Strains – Slip, trips and falls are some of the leading causes of injuries in the trucking industry. This course provides information on some of the causes and preventive measures relevant to trucking and applicable in the workplace or in daily life. We also talk about sprains and strains as a cause or effect of slips, trips, and falls.
Make sure to visit our Safety Talks page for more valuable articles like this one!

